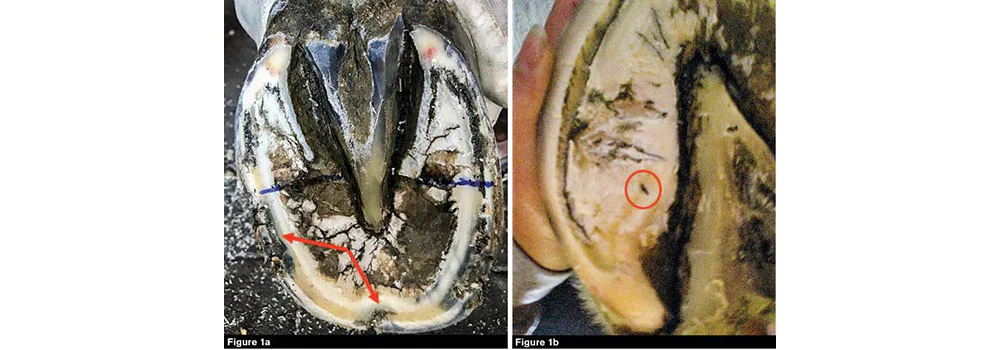
An abscess in the hoof causes significant pain for horses. It arises from a bacterial infection that leads to the accumulation of pus within the hoof structure. To effectively treat this condition, it is crucial to accurately identify the borders of the hoof abscess. This article explores the necessary steps and considerations involved in locating these boundaries with precision.
Identifying Hoof Abscess Borders: Mapping and Management
Precisely Picturing and Managing Hoof Abscess Borders
Effectively addressing a hoof abscess hinges on the accurate identification and delineation of its borders. Given the migratory nature of hoof abscesses, a comprehensive evaluation that combines visual inspection with radiography or debridement is recommended to ascertain the full extent of the abscess.
The Vital Role of Adequate Drainage
Facilitating proper drainage is paramount when dealing with hoof abscesses. Ensuring a reliable path for abscess fluid release is achieved by creating channels or openings in the hoof, allowing pus to escape. In tandem with drainage, the use of antiseptic packing promotes the healing process.
Metronidazole Packing: Battling Bacteria
Some veterinarians turn to metronidazole packing to combat anaerobic bacteria within hoof abscesses. Metronidazole, an antibiotic, can be packed into the abscess cavity to eliminate bacteria and foster healing. Nevertheless, it’s important to bear in mind that systemic antimicrobial use may carry the risk of the infection receding, potentially resurfacing later.
Betadine Soak: A Soothing Solution
Immersing the hoof in a 1% betadine solution enriched with epsom salts proves advantageous for drawing out deeper-infected tracts within the hoof. Betadine, an antiseptic solution, excels at bacteria eradication, while epsom salts contribute to inflammation reduction and enhanced drainage.
Multiple Tracts and Osteomyelitis Considerations
In scenarios where initial treatment proves ineffective, the presence of multiple tracts or the emergence of osteomyelitis in the third phalanx may be the culprit. In such instances, a radiographic examination becomes imperative for precise diagnosis and the formulation of an advanced treatment strategy.